The Science of Healing: 5 Amazing Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy You Need to Know
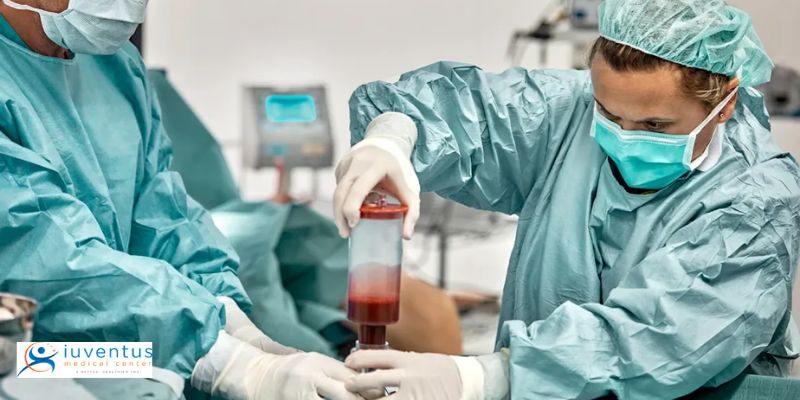

In recent years, regenerative medicine has witnessed groundbreaking advancements, with stem cell therapy taking center stage as a revolutionary approach to healing various medical conditions. Stem cells, the building blocks of life, can transform into specialized cells and repair damaged tissues. This article explores five incredible benefits of stem cell therapy that are changing the landscape of modern medicine and offering new hope to patients with chronic ailments and injuries.
The 5 Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy You Need to Know
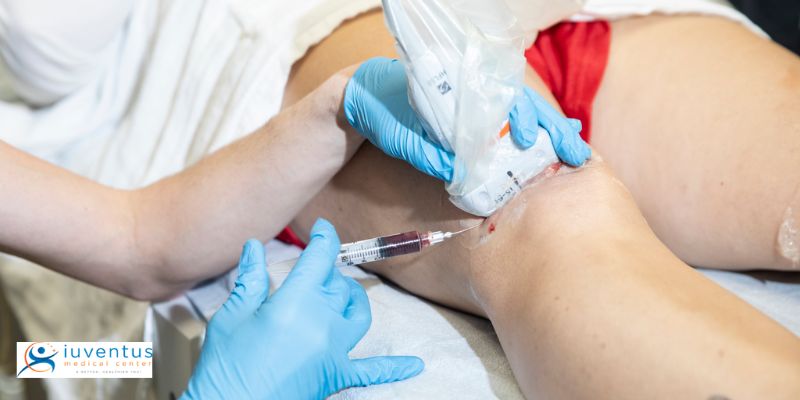
1. Tissue Regeneration and Repair
Stem cell therapy’s foremost benefit lies in promoting tissue regeneration and repair. Stem cells can differentiate into specialized cell types, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, or cartilage cells, depending on the body’s needs.
When injected into injured or damaged tissues, these adaptable cells actively contribute to the repair process, fostering the regeneration of healthy tissues and restoring functionality to affected areas. This has proven invaluable in treating conditions like osteoarthritis, spinal cord injuries, and heart muscle damage, offering patients a chance to regain lost mobility and alleviate pain.
Moreover, stem cells’ regenerative properties offer an attractive alternative to conventional treatments that may only manage symptoms without addressing the underlying cause. By targeting the root of the problem and stimulating the body’s natural healing processes, stem cell therapy presents a promising avenue for long-term recovery and improved quality of life.
2. Reduced Risk of Rejection
Traditional organ transplants often face the challenge of organ rejection due to the body’s immune system recognizing the transplanted tissue as foreign. However, stem cell therapy offers a promising solution to this problem.
Unlike conventional transplants, stem cells used in treatments can be obtained from the patient’s body (autologous transplantation) or from donors with matching tissue types (allogeneic transplantation).
In autologous transplantation, the patient’s stem cells are processed and re-injected into the affected area. Since these cells are a genetic match, the risk of rejection is significantly reduced.
Similarly, in allogeneic transplantation, stem cells from carefully selected donors with matching tissue types are used, further minimizing the risk of rejection. This breakthrough in reducing transplant-related complications makes stem cell therapy a safer and more viable option for patients needing tissue replacement or regeneration.
3. Treatment of Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases like diabetes, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis pose significant challenges to patients and medical professionals. Stem cell therapy has shown promising results in the treatment of these conditions.
By replacing damaged cells or stimulating the body’s natural healing processes, stem cell therapy offers potential relief and improved quality of life for individuals with chronic diseases.
Researchers are exploring various stem cell types and their potential to address specific conditions. For instance, in the case of diabetes, pancreatic beta cells derived from stem cells could help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the need for insulin injections.
In Parkinson’s disease, stem cells could replenish dopamine-producing neurons lost in the brain, potentially alleviating motor symptoms. Although research is ongoing, early studies have provided encouraging evidence of the therapy’s efficacy in managing these complex conditions, providing hope for more effective treatments in the future.
4. Accelerated Wound Healing
Chronic and non-healing wounds can lead to severe complications and prolonged patient suffering. Stem cell therapy has emerged as a powerful tool to expedite wound healing and offer a ray of hope to those struggling with persistent wounds. When applied to wounds, stem cells release various growth factors and anti-inflammatory agents, creating a favorable environment for tissue regeneration and repair. These bioactive substances help attract other cells involved in the healing process, such as fibroblasts and endothelial cells, to the wounded site, stimulating the formation of new blood vessels and promoting tissue growth.
In diabetic ulcers, where impaired blood flow and compromised healing mechanisms are standard, stem cell therapy has shown remarkable success. By enhancing the body’s natural ability to heal, stem cells can significantly accelerate wound closure and reduce the risk of infections, preventing potential amputations and improving the patient’s quality of life.
5. Neurological Disorders and Brain Injuries
Neurological disorders and brain injuries present some of the most challenging medical conditions to address effectively. However, stem cell therapy also brings hope to this field of medicine.
Stem cells have the potential to differentiate into various neural cells, including neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, which are crucial for brain function. By transplanting stem cells into the brain, researchers and medical practitioners aim to restore damaged neural circuits and improve neurological processes.
In conditions like Alzheimer’s, where neurons progressively degenerate, stem cell therapy offers the possibility of replenishing lost neurons and slowing disease progression.
Stem cells injected into the affected brain regions could aid tissue repair and enhance functional recovery for stroke patients. Similarly, traumatic brain injuries, which often result in permanent damage, could benefit from stem cell therapy by promoting regeneration and reestablishing neural connections.
While research in this area is still at an early stage, the potential for stem cell therapy to revolutionize the treatment of neurological disorders and brain injuries holds promise for millions worldwide, seeking better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Wrapping Up
Stem cell therapy’s astounding benefits have captured the medical community’s and patients’ attention worldwide. Its potential for tissue regeneration, reduced rejection risk, treatment of chronic diseases, accelerated wound healing, and neurological disorder management holds promise for the future of medicine.
As research and technology advance, stem cell therapy will likely transform healthcare, offering renewed hope and improved quality of life for countless individuals grappling with medical challenges.
However, despite the remarkable progress in the field, it is essential to continue rigorous scientific studies, adhering to ethical standards and regulatory protocols, to fully understand the therapy’s safety, efficacy, and long-term effects.
With ongoing research and collaboration between medical experts, stem cell therapy has the potential to unlock even more benefits and change the lives of patients worldwide, ushering in a new era of healing and medical possibilities.
