Empowering the Immune System: Stem Cell Therapy’s Role in Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases pose significant challenges to individuals, often resulting in chronic pain, organ damage, and a decreased quality of life. These conditions arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues.
Traditional treatment options, such as immunosuppressant medications, have limitations and may cause adverse effects. However, a promising avenue that holds immense potential in the field of autoimmune disease treatment is stem cell therapy.
With their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, stem cells offer a groundbreaking approach to empowering the immune system and provide a ray of hope for patients struggling with autoimmune diseases.
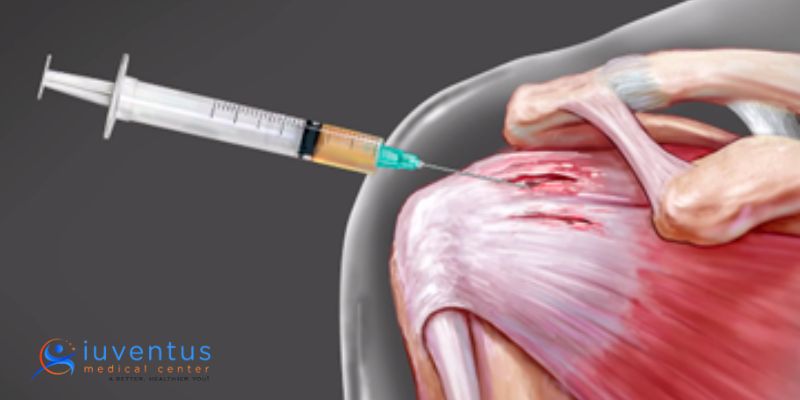
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that utilizes stem cells to treat or prevent diseases or injuries. Stem cells are unique cells that can self-renew and differentiate into various specialized cell types in the body. They can replace damaged or dysfunctional cells, promote tissue repair, and restore normal organ function.
Stem cells can be derived from different sources, including embryos, fetal tissue, umbilical cord blood, and adult tissues. Each source has its advantages and limitations. Embryonic stem cells, for example, can differentiate into any cell type in the body and offer great regenerative potential.
However, their use raises ethical concerns due to the destruction of embryos. On the other hand, adult stem cells are found in various tissues, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and blood. They have a more limited differentiation capacity but can still differentiate into multiple cell types related to their tissue of origin.
The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases
1. Repairing Tissue Damage
Autoimmune diseases often destroy healthy tissues and organs. Stem cell therapy offers a unique advantage by promoting tissue repair and regeneration.
When administered, stem cells can migrate to the affected tissues and differentiate into the specific cell types required for repair. This regenerative capacity of stem cells can reverse the damage caused by autoimmune attacks.
Moreover, stem cells can secrete various growth factors and cytokines that create a favorable environment for tissue healing. These factors promote the growth of new blood vessels, enhance cell survival, and stimulate the production of extracellular matrix components.
As a result, stem cell therapy can facilitate tissue remodeling and regeneration, potentially restoring the functionality of damaged organs in autoimmune disease patients.
2. Regulating the Immune System
One of the primary roles of stem cell therapy in autoimmune diseases is to regulate the immune system. Stem cells possess immunomodulatory properties, which can influence and modify the immune response.
By interacting with immune cells and releasing signaling molecules, stem cells can promote immune balance and dampen excessive inflammation. This ability is particularly crucial in autoimmune diseases, where an overactive immune system contributes to tissue damage.
Studies have shown that stem cells can inhibit the proliferation and activation of immune cells responsible for the autoimmune response. They can also induce the generation of regulatory T cells, a subset of immune cells that help maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmunity.
By regulating the immune system, stem cell therapy can help mitigate the progression of autoimmune diseases, reduce symptoms, and improve overall well-being.
3. Resetting the Immune System
Another intriguing aspect of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases is its potential to reset the immune system. Autoimmune diseases occur due to a loss of immune tolerance, where the immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells.
Stem cells can help restore this balance by promoting the development of a new immune repertoire. Introducing healthy stem cells into the body can stimulate the regeneration of immune cells, leading to a “reboot” of the immune system.
This immune system reset can profoundly impact autoimmune diseases, potentially interrupting the autoimmune process and preventing further tissue damage. While the mechanism behind this reset is still under investigation, its therapeutic potential is immense.
Stem cell therapy offers a unique opportunity to reshape the immune system’s response, providing long-lasting benefits for individuals battling autoimmune diseases.
4. Modulating Inflammation
Inflammation is a hallmark of autoimmune diseases, contributing to tissue damage and symptoms such as pain, swelling, and redness. Stem cell therapy offers the potential to modulate this inflammatory response, providing relief to patients suffering from autoimmune conditions.
Stem cells have been found to produce anti-inflammatory factors that can suppress the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and inhibit the activation of immune cells involved in the inflammatory cascade.
Furthermore, stem cells can interact with the surrounding cells and tissues, influencing their behavior and promoting an anti-inflammatory microenvironment.
By modulating inflammation, stem cell therapy can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the severity of autoimmune disease flares. This can significantly improve the quality of life for patients, allowing them to manage their condition better and potentially reducing their reliance on immunosuppressive medications.
5. Personalized Treatment Approach
Stem cell therapy offers a personalized treatment approach for autoimmune diseases. Each patient’s immune system and disease manifestations are unique, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all treatment strategy.
However, stem cells can be obtained from various sources, including the patient’s body (autologous stem cells) or compatible donors (allogeneic stem cells). This flexibility allows for tailored treatment plans based on individual needs.
Autologous stem cell therapy involves harvesting the patient’s stem cells, which are then processed and reintroduced into the body. This approach minimizes the risk of immune rejection and eliminates ethical concerns associated with using donor cells.
On the other hand, allogeneic stem cell therapy utilizes stem cells from a compatible donor, providing a readily available source of cells for treatment. This option may be beneficial for patients who do not have suitable autologous stem cell sources.
By tailoring the stem cell source and treatment approach to each patient, personalized stem cell therapy maximizes the potential for therapeutic success. It improves treatment outcomes for individuals with autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy holds immense promise in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. By regulating the immune system and promoting tissue repair, stem cells have the potential to empower the body’s natural defenses against these debilitating conditions.
